Investing in mutual funds has become increasingly popular in recent years, with thousands of options available to investors. But with so many choices, it can be challenging to determine which funds are the right fit for your investment goals. In this article, we will cover the basics of mutual funds, including different types of funds, investment strategies, and plan options.
What are Mutual Funds?
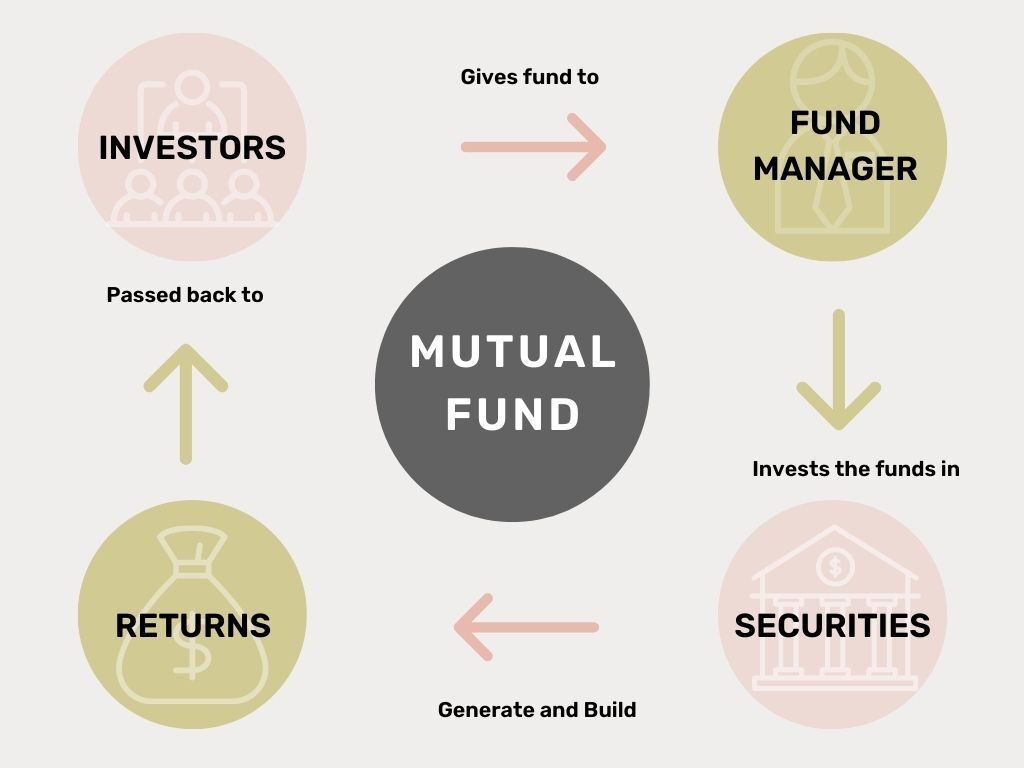
A mutual fund is a financial vehicle that pools funds from shareholders to invest in a range of securities, including stocks, bonds, money market instruments, and gold.
A professional fund manager is responsible for overseeing the fund’s investments and making decisions about what securities to buy or sell.
Mutual funds allow investors to gain exposure to a diversified portfolio of securities, without having to manage the investments themselves.
Why Invest in Mutual Funds?
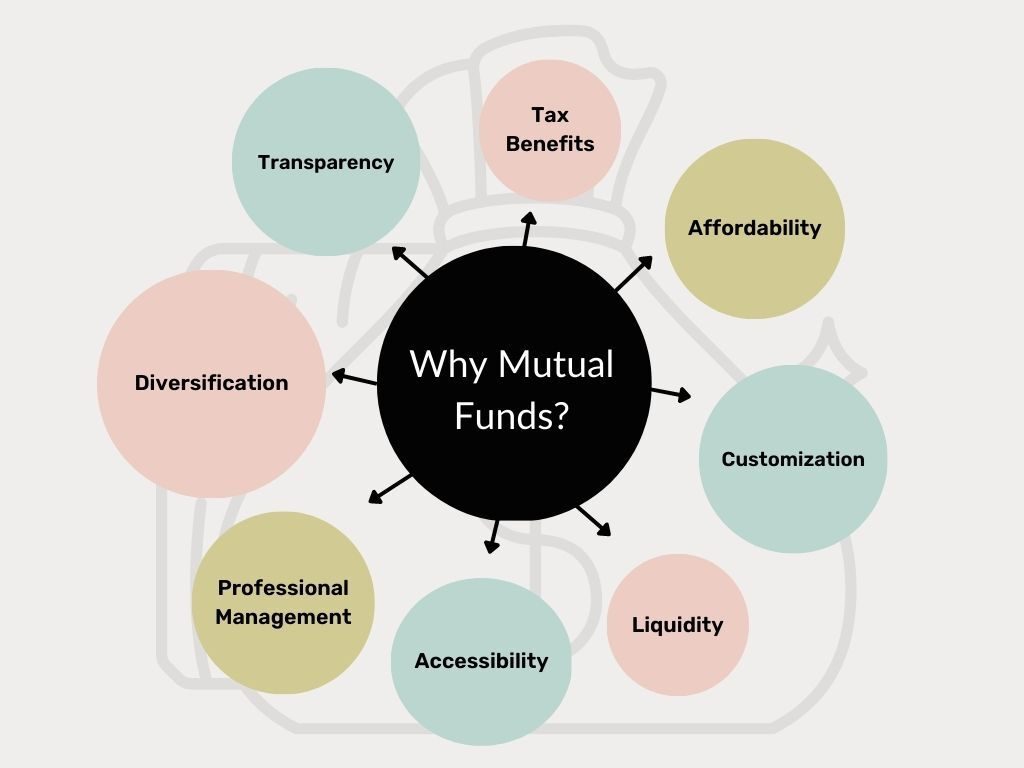
Cost-Effective: Mutual funds can be a cost-effective way to invest in a diversified portfolio of securities. The cost of purchasing individual securities can be prohibitive for most investors, whereas mutual funds allow investors to pool their resources to gain exposure to a range of securities at a lower cost.
Expert Portfolio Management: Mutual funds are managed by professional fund managers who have the expertise to make investment decisions based on their market knowledge, research, and analysis.
Investor-Friendly: Mutual funds are available for purchase through a range of channels, including online platforms, banks, and financial advisors.
Easy Redemption: Mutual funds are highly liquid, meaning investors can easily buy and sell shares of the fund as needed.
Tax-Friendly: Mutual funds offer tax benefits such as tax exemptions on capital gains and dividends received from the fund.
Key Mutual Fund Concepts
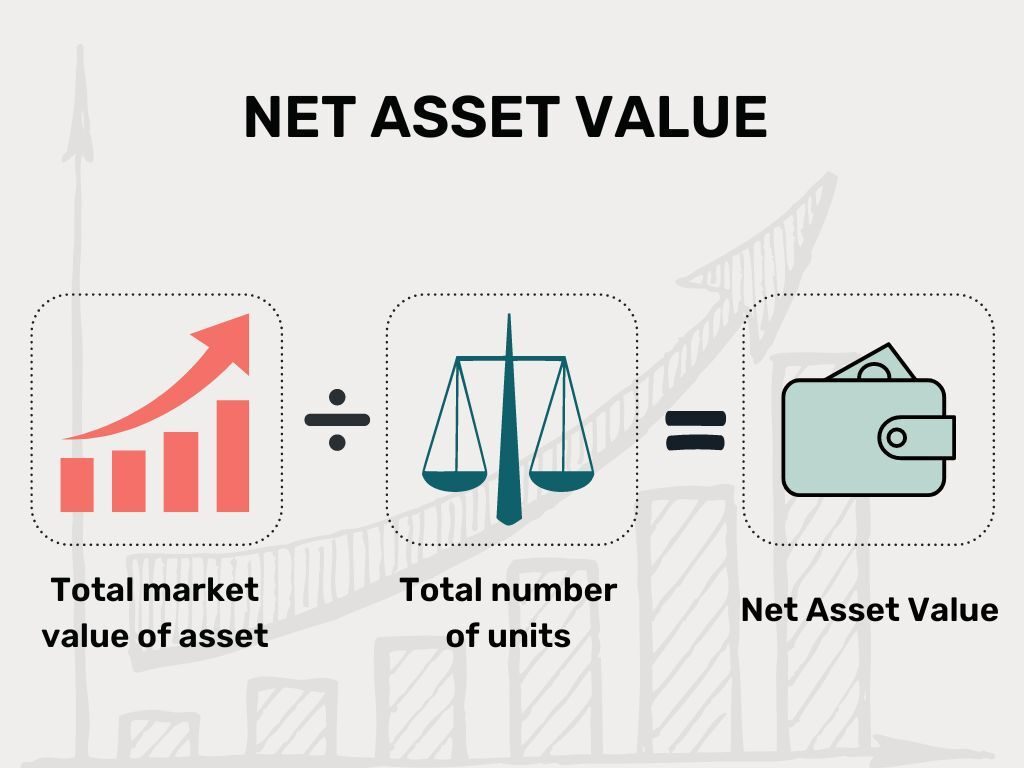
Net Asset Value (NAV): NAV represents the market value per share for a specific mutual fund scheme. It is calculated as the total market value of a scheme divided by the total number of units of the scheme on a given date.
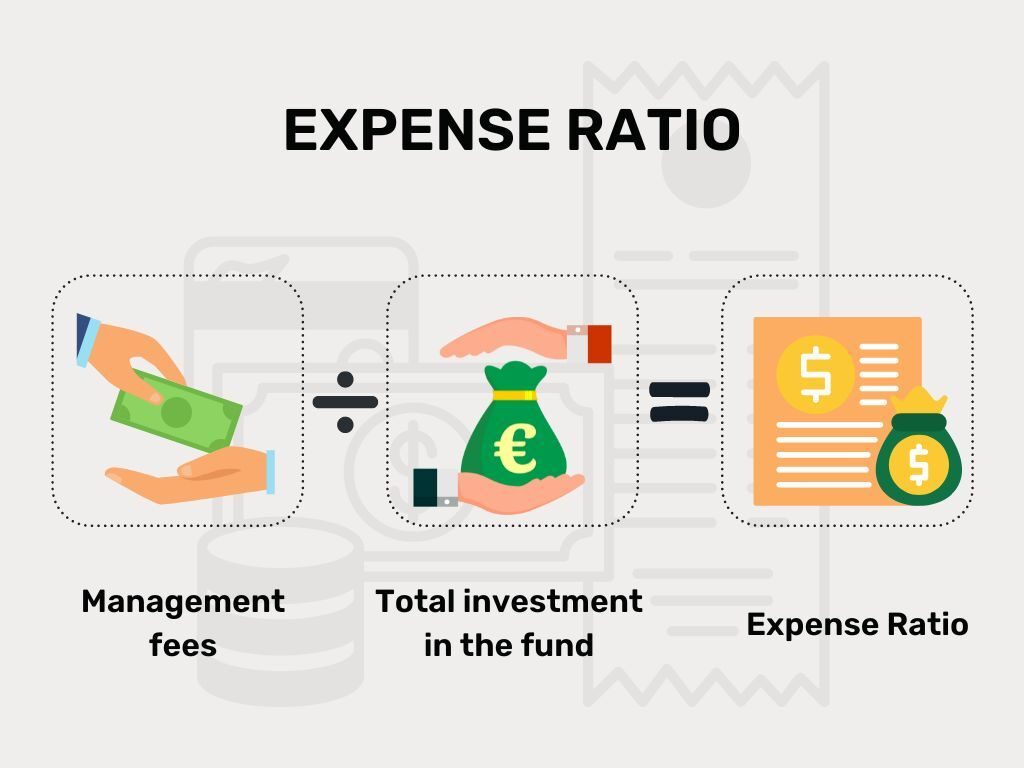
Expense Ratio: The expense ratio is the percentage of your investment that you pay to the Asset Management Company (AMC) as a fee for managing your investments. It represents the cost per unit for the operation and management of the mutual fund.
Direct vs Regular Mutual Fund Plans
Direct Plans: Direct plans are purchased directly from the AMC without intermediaries. Investing in direct plans can be done online via the AMC’s website, and they have lower expense ratios compared to regular plans.
Regular Plans: Regular plans are purchased through mutual fund distributors, who provide services like helping investors decide which schemes to invest in. The expense ratios for regular plans are higher for this reason.
Should You Choose Regular Plans or Direct Plans?
Choosing between regular and direct plans depends on your investment knowledge and comfort level. Regular plans offer guidance from a distributor but come with higher expense ratios. In contrast, direct plans have lower expense ratios but require investors to have the ability to decide which mutual funds are right for them.
Growth vs Dividend Options
Growth Options: In the growth option, the mutual fund scheme reinvests the profits made by the scheme instead of paying them out to investors. This option is ideal for long-term investors.
Dividend Options: In the dividend option, the profits made by the mutual fund scheme are paid out to investors at regular intervals such as annually, daily, monthly, or quarterly.
Exit Load
Exit load is a fee charged by the AMC when investors partially or fully exit a scheme within a specific period from the date of investment. Some schemes do not charge any exit fees.
Types of Mutual Funds
Mutual funds are broadly classified based on the underlying assets that they invest in. Here are the four primary types of mutual funds:
– Equity Mutual Funds
– Debt Mutual Funds
– Money Market Funds
– Balanced or Hybrid Funds
Equity Mutual Funds
Equity mutual funds invest a major portion of their assets in equity shares of companies. These funds carry a higher level of risk compared to other types of mutual funds.
Equity mutual funds are ideal for long-term wealth creation and are recommended for investors who are willing to accept higher levels of risk.
Debt Mutual Funds
Debt mutual funds invest in fixed income instruments such as bonds, debentures, and government securities. These funds carry a lower level of risk compared to equity mutual funds.
Debt mutual funds are recommended for investors who are looking for a steady stream of income and exposure to fixed income products.
Money Market Funds
Money market mutual funds invest in highly liquid instruments such as Treasury Bills, Commercial Papers, and Certificates of Deposits.
These funds are recommended for investors who want to park their money for the short term and earn a slightly higher return compared to a savings account.
Balanced or Hybrid Funds
Balanced or Hybrid funds invest in both equity and debt instruments. These funds are ideal for investors who want to have a balanced portfolio and exposure to both equity and debt markets.
Balanced funds carry a moderate level of risk compared to equity and debt mutual funds.
Open-ended vs Close-ended funds
Mutual funds can be classified based on their structure:
Open-ended Funds
Open-ended funds allow investors to enter and exit the fund as per their convenience. The mutual fund company facilitates the entry and exit of investors.
Close-ended Funds
Close-ended funds are open for subscription only during the initial offer period and have a specified tenor and fixed maturity date (similar to a fixed-term deposit). Units of close-ended funds can be redeemed only on maturity.
Passive/Index Funds vs. Active Funds
Mutual funds can also be classified based on their investment style. Here are the two primary types of mutual fund investment styles:
Passive/Index Funds
Passive or index funds mimic a certain market index. These funds do not have a fund manager and follow the entry and exit of the underlying index. Passive funds are a cost-effective way to invest in the markets.
Active Funds
Active funds have an active fund manager who picks and chooses investments with the aim of beating the fund’s stated benchmark or index. These funds carry a higher expense ratio compared to passive funds.
Wish to learn more about active vs passive funds? Here’s a blog we have written on the subject:
https://www.mprofit.in/blog/2023/04/active-vs-passive-funds-explained/
Conclusion
Mutual funds offer investors an excellent opportunity to gain exposure to a wide range of asset classes and improve their asset allocation.
As an investor, it is important to carefully research and choose the right mutual fund that aligns with your investment goals and risk appetite.
Start by determining your investment horizon and risk tolerance and consult a financial advisor if needed. Happy investing!
Comments